Document Retrieval to Deep Learning - The Evolution of Vector Databases.
Hi All,
If you are following the advancement in the field of AI recently, it is impossible not to notice the enormous growth in data/corpus size. In particular, recent breakthroughs in the field of unstructured data, such as large language models like GPT-3, protein folding prediction systems like AlphaFold, and differentiable programming frameworks like DELLE, have demonstrated the need for efficient storage and fast retrieval of massive amounts of high-dimensional data. This is where vector databases come into the picture.
In recent years, machine learning has seen significant advancements in the form of deep learning algorithms. These algorithms often involve working with high-dimensional data in the form of vectors. As a result, vector databases have become an important tool for machine learning practitioners and vector embedding is a key to it.
Vector embedding allows us to convert text, images etc. into numbers that can be easily processed by computers. These numerical representations are designed in such a way that similar objects are represented by similar vectors, and the distance between the vectors reflects the degree of similarity between the objects. Vector embeddings are leveraged for tasks such as clustering, classification, recommendation etc.
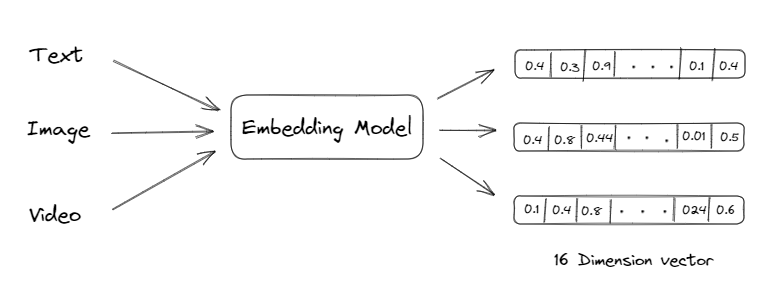
History of Vector Databases
Vector databases have been around for several decades, but their use has increased significantly in recent years due to the rise of deep learning algorithms. The first vector database was introduced in the 1970s for use in information retrieval. The database stored document vectors to enable fast similarity searches. In the 1990s, vector databases were also used in data mining and clustering algorithms.
Need for Vector Databases in Machine Learning
Vector databases are essential for many machine learning algorithms, particularly those that involve working with high-dimensional data. These algorithms require efficient similarity searches, classification, and clustering of data points, which can be achieved using vector databases. For example, in image retrieval, deep learning models can learn to represent images as high-dimensional vectors and vector databases can be used to efficiently search for similar images based on these representations. I have leveraged the below image from my previous blog. Any image can be represented as a collection (high-dimensional vector) of numbers.
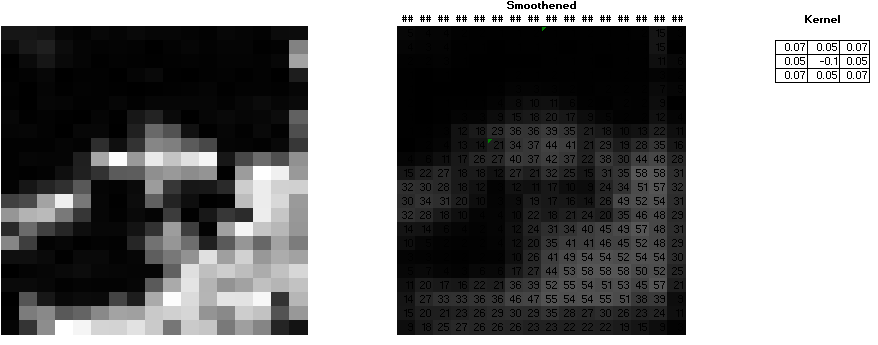
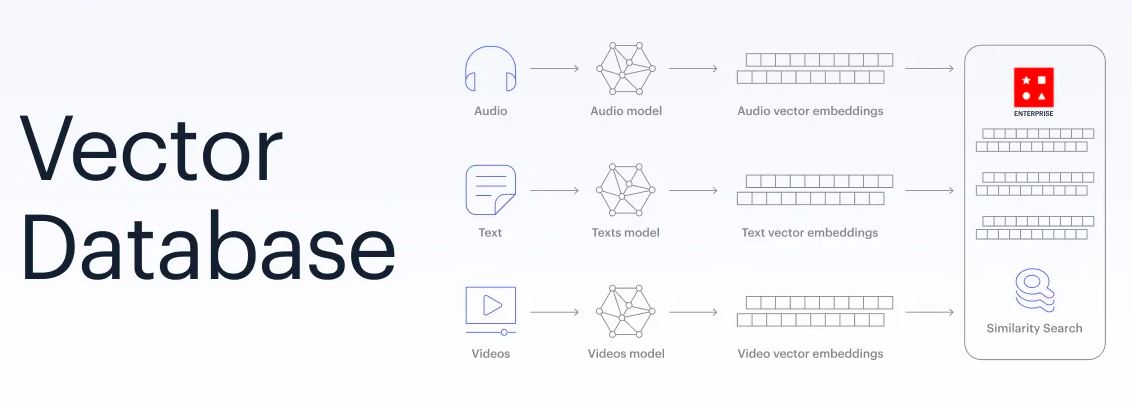
How Data is Stored in Vector Databases
Vector databases store data using a variety of data structures, such as k-d trees, hash tables, and inverted indices. These data structures allow for efficient similarity searches, classification, and clustering of high-dimensional data. Each data structure has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of data structure depends on the specific application. One popular vector database is Apache Cassandra, which is a distributed NoSQL database that can store and manage large amounts of vector data. Another example is Faiss, a library for efficient similarity search and clustering of dense vectors.
Search Algorithms
There are several search algorithms for efficient retrieval of similar vectors or similarity search. Some of the commonly used search algorithms in vector databases are:
-
Euclidean Distance: This is a distance-based search algorithm where vectors are compared based on straight-line distance between two points in n-dimensional space. The algorithm involves calculating the Euclidean distance between the query vector and all vectors in the database, and then returning the vectors with the smallest distances as the search results.
-
Cosine Similarity: Cosine similarity is a measure of similarity between two vectors based on the cosine of the angle between them. The algorithm involves calculating the cosine similarity between the query vector and all vectors in the database and then returning the vectors with the highest cosine similarity values as the search results.
-
Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH): LSH is a popular approximate nearest neighbor search algorithm that uses hashing functions to map similar vectors to the same buckets with high probability. LSH is particularly useful for large-scale vector databases as it can significantly reduce the number of pairwise comparisons required for similarity search.
-
k-d Tree: A k-d tree (k-dimensional tree) is a data structure that partitions space in order to organize points in a k-dimensional space. It can be used for efficient range search and nearest neighbor search in vector databases. The k-d tree recursively divides the space into axis-aligned hyperrectangles, and stores the vectors at the leaf nodes. Nearest neighbor search can be performed by traversing the tree and pruning branches that are unlikely to contain the nearest neighbor.
-
Product Quantization (PQ): PQ is a popular technique for approximate nearest neighbor search in vector databases. It involves partitioning each vector into multiple subvectors, quantizing each subvector separately, and then combining the quantized subvectors to form a compact binary code. PQ allows for efficient storage and retrieval of high-dimensional vectors, and is widely used in applications such as image retrieval and multimedia databases.
-
Hierarchical Navigable Small World Graphs (HNSW): HNSW is a graph-based algorithm for approximate nearest neighbor search that organizes vectors in a hierarchical graph structure. The algorithm constructs a graph of vectors by connecting similar vectors with edges, and organizes the graph in multiple levels of resolution. HNSW allows for efficient navigation and pruning of the search space, and is known for its high search efficiency and scalability.
Thank you!!


Leave a comment